XS Japan 2008 BitVisor English
- 1. Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 マスタ サブタイトルの書式設定 Takahiro Shinagawa University of Tsukuba Introduction to BitVisor and Comparison with Xen 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008
- 2. What is BitVisor ? A VMM featuring security functionalities Has been developed by “Secure VM Project” A R&D project with governmental support ▪ Initiated by NISC (National Information Security Center) ▪ Funded by SCF of MEXT ▪ SCF: Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology MEXT: Ministry of education, culture, sports, science and technology developed from scratch (an all-Japanese product) Several universities and organizations are involved ▪ * VMM: Virtual Machine 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 22 Monitor
- 3. Background & Purpose Increasing threats of information leakage From lost or stolen PCs and USB memories Through the Internet Via viruses and P2P file-sharing software ▪ Using a VMM to prevent information leakage Enforce encryption and authentication Encrypt storages and networks ▪ ▪ Authenticate with smart cards 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 33
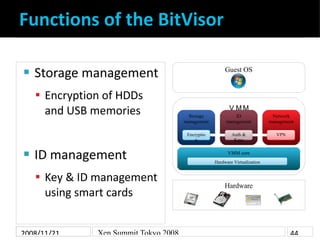
- 4. Functions of the BitVisor Storage management Guest OS Encryption of HDDs and USB memories VMM Storage ID Network management management management Encryptio Auth & VPN n Keys ID management VMM core Hardware Virtualization Key & ID management Hardware using smart cards 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 44
- 5. Assumptions behind Design Decisions Security of the VMM itself is important VMM should be kept as small as possible Used in desktop environments Windows is the target OS to be secured Limited development cost & period 3 years, 5 full-time researchers, limited budget 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 55
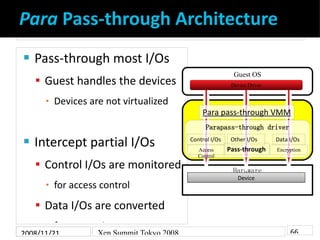
- 6. Para Pass-through Architecture Pass-through most I/Os Guest OS Guest handles the devices Device Driver Devices are not virtualized ▪ Para pass-through VMM Parapass-through driver Intercept partial I/Os Control I/Os Other I/Os Data I/Os Pass-through Access Encryption Control Control I/Os are monitored Hardware Device for access control ▪ Data I/Os are converted ▪ for encryption 66 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008
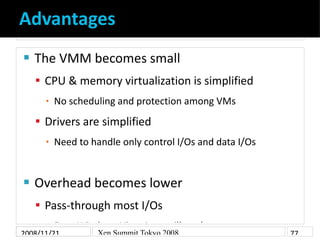
- 7. Advantages The VMM becomes small CPU & memory virtualization is simplified No scheduling and protection among VMs ▪ Drivers are simplified Need to handle only control I/Os and data I/Os ▪ Overhead becomes lower Pass-through most I/Os ▪ Even Windows Vista Aero will work 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 77
- 8. Disadvantages Multiple OSes cannot run simultaneously The guest OS directly handles the devices -> Acceptable since the target is desktop computers Hardware support is limited A driver is required for each (monitored) device -> Acceptable in office (government) environments 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 88
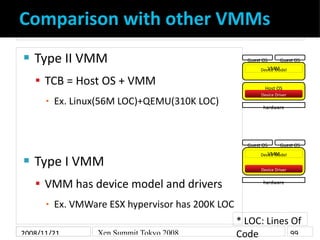
- 9. Comparison with other VMMs Type II VMM Guest OS Guest OS VMM Device Model TCB = Host OS + VMM Host OS Device Driver Ex. Linux(56M LOC)+QEMU(310K LOC) ▪ hardware Guest OS Guest OS VMM Device Model Type I VMM Device Driver VMM has device model and drivers hardware Ex. VMWare ESX hypervisor has 200K LOC ▪ * LOC: Lines Of Code 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 99
- 10. Comparison with Xen (Size) Xen Guest Domain 0 VMM (hypervisor) is relatively small OS Device Model Device Driver About 100 K LOC [Murray et al. VEE2008] ▪ VMM hardware TCB is not necesssarily small Including Domain 0 ▪ BitVisor VMM is small ▪ VMM core has about 20 K LOC 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1010
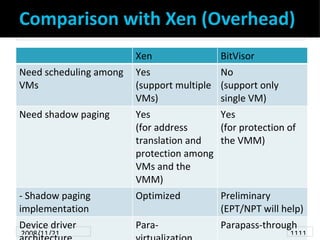
- 11. Comparison with Xen (Overhead) Xen BitVisor Need scheduling among Yes No VMs (support multiple (support only VMs) single VM) Need shadow paging Yes Yes (for address (for protection of translation and the VMM) protection among VMs and the VMM) - Shadow paging Optimized Preliminary implementation (EPT/NPT will help) Device driver Para- Parapass-through 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1111
- 12. Experimental Setup Hardware Intel Core 2 Duo E8600 (3.33GHz) 4GB memory 10,000rpm HDD (Western Digital Raptor WD740GD) ▪ Software VMM: BitVisor 0.3 (64bit) Guest OS: Fedora 9Tokyo 2008 Windows Vista (64bit) Xen Summit (64bit), 2008/11/21 1212
- 13. Experimental Result 1 Now Printing 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1313
- 14. Experimental Result 2 Now Printing 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1414
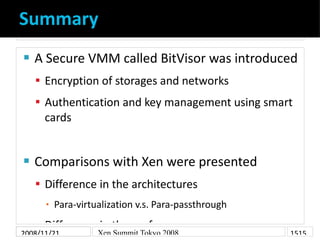
- 15. Summary A Secure VMM called BitVisor was introduced Encryption of storages and networks Authentication and key management using smart cards Comparisons with Xen were presented Difference in the architectures Para-virtualization v.s. Para-passthrough ▪ Difference in the performances 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1515
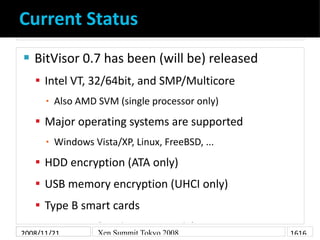
- 16. Current Status BitVisor 0.7 has been (will be) released Intel VT, 32/64bit, and SMP/Multicore Also AMD SVM (single processor only) ▪ Major operating systems are supported Windows Vista/XP, Linux, FreeBSD, ... ▪ HDD encryption (ATA only) USB memory encryption (UHCI only) Type B smart cards IPsec VPN (Intel PRO100 only) 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1616
- 17. Download http://www.securevm.org/ 2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1717






![Comparison with Xen (Size)
Xen
Guest
Domain 0
VMM (hypervisor) is relatively small OS
Device
Model
Device Driver
About 100 K LOC [Murray et al. VEE2008]
▪ VMM
hardware
TCB is not necesssarily small
Including Domain 0
▪
BitVisor
VMM is small
▪ VMM core has about 20 K LOC
2008/11/21 Xen Summit Tokyo 2008 1010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/takahiroshinagawaxensummittokyo2008shinaen-090504211019-phpapp02/85/XS-Japan-2008-BitVisor-English-10-320.jpg)