My first program and the
first computer
The first
program I ever wrote was malware. That is if malice as intent and effect make
software malware. I was around 10 years old and my father had just convinced my
mom that purchasing a monitor for his New Brain computer would not ruin our
family. New Brain was a 32kb memory computer, with a terrible keyboard, 11 char
calculator display and programmable in basic. To store programs and data my
father had soldered around in my cassette recorder. The newly purchased monitor
was monochrome and small. With monochrome I don’t mean black and white. I mean
dark brown and beige yellowish. I was at least as fascinated with the computer
as my geek father. It was probably no accident that I immediately realized that
it was the perfect instrument for mischievous behavior. The program that I’d
written was:
10 print
“Karen is stupid”
20 goto 10
Karen is my
older sister. And it's worth noting that even this simple program ran slow enough that you could see it scrolling down the screen. In those days - probably 1984ish - computers where magical things
and one better listen when they had computed something. My sister screamed with
rage - which was cool since she probably deserved it
Commodore
A few years
later my father had upgrade the “New Brain” to a Commodore C128. By now I was
fairly good in writing basic programs and was only half bad in Comal 80. But I didn’t want to code. I wanted to crack
games and have my “nickname” on the start up screen of the games everybody else
played. My problem was that I need a machine code monitor and the only machine
code monitor that I knew about for C64 was the “Final Cartridge”. I wasn’t
allowed to buy it. So I instead booted in C128 mode and started monitor.
Anybody who has ever used “monitor” has either given up quick or committed
suicide at least that's what I think. Especially since I (and I assume most other people) did not have any C128 software to
be debugged. I gave up.
Early PC days
1992 and I
had my first break actually “reverse engineering” something. I’d stumbled upon
a text called “act-13.txt”. It was about cracking PC games using debug.exe. The
irony was that debug.exe was incredibly powerful and terrible at the same time.
It served as hex editor, disk editor, debugger,disassembler and assembler build into one
terrible scrolling user interface. The act-13.txt described how you used
debug.exe to search through a binary file for “CD 13” that is interrupt 13.
You’d have to have sufficient luck to also get hold of Ralph Browns interrupt
list to have a chance of figuring out how that interrupt worked. Ralph Brown’s
list was the documentation for programming the PC at that point. Say the MSDN
of the day. Remember you had to find another old guy your age with the same
interest who’d actually copy it on a 3.5” diskette for you. I were lucky. Copy
protection in those days mostly worked around either letting the user enter a
code from a code sheet or have the game distributed on a floppy diskette that
had been formatted off spec. For the diskette copy protection we’d thus look
for stuff that read physically from the diskette and this was interrupt 13. So
search the entire code for int 13, then disassemble, see if you could figure
out what it was doing and usually changing a JC/JNC into two nops or a JMP. If
you’re a modern hacker you’re probably wondering what the carry flag has to do
with anything. But in those day the most common call style was for bool to be
returned in the carry flag using CLC and STC instructions respectively.
Call xxxx:xxxx
jnc yyyy
was a
common construct. When you see the call xxxx:xxxx chances are you'd see the far
call instruction as an exotic instruction, but back then far calls where used
all the times as it was the only way to cross 64kb boundaries in code.
The first virus
In the
early 90ies I became terribly obsessed with biological inspired terminology in
computers. Virus, worms and artificial intelligence. These terms where in every
computer journal you could imagine all the time. Dark Avenger and his nemesis
Vesselin Bontchev where both heroes of mine. Pushing the boundaries of what
could be done, on the verge of changing the world. I wanted to write a virus,
but had absolutely no clue. So I tried to code up a neural network and thought
at the time I'd succeeded. In retrospect I believe the chance of that being
true is around 0. I made a good effort though, but I should've kept quiet - the
comment in the school yard that "I'd gotten my inteligence to work"
was too much of a softball not to follow me for a couple of years. I must've
been around 14 at the time. Viruses where difficult to find, despite my best
efforts. My first break through was getting an anti virus. IBM
antivirus 2.0 if I recall correctly. It came with a human readable signature
file with an jaw dropping 23 signatures. By playing around in this file and
Norton Disk Edit I managed to have it detect other files as viruses. Soon after
I got infect by the "form.a" virus and figured out how to remove it
by running "sys.exe". Form was
a boot sector virus that spread when computers booted from 3.5" floppy
drives. During the boot process it hooked interupts and could thus propagate it
self when DOS called on these interupts to mount another floppy disc.
Ironically boot sector viruses was amongst the first viruses and is the
immediate ancestor to boot kits today - now considered a more advanced type of
malware.
Getting connected
Within a
year of moving out to attend university I were cohabiting with 4 computer geeks
like myself. It turned into a massive skill upgrade for me due to synergies and
because we ran the BBS "Psychic Damage" which at it's prime was
probably the best (1 Zyxel 19k2 node and 1 ISDN 64kb node) H/P/A/V BBS in
Denmark. HPAV stood for Hacking, Phreaking, Anarchy (explosives and drugs) and
Virus. We had tons of documents on hacking, hacking logs, password files. We
however also had house rules. No hacking, no virus. So even though we had a
large achieve of virus I was banned from examining them. I stuck by the rules
because, I did not want to lose moral high ground on the hacking question. At
least one of the other guys would've loved to hack anything and there is little
doubt that he was capable of doing it. The first waves of hacking busts by what
seemed like Denmarks only security expert at the time, Joergen Bo Madsen, where
highly publicized. And Mr. Madsen had mentioned in a lecture that our BBS had
the password file from the department of computer science at my university
lying around on our BBS. He was right too, but I haven't got a clue how he
could've known and that kept me a bit scared. Never the less I would have the
opportunity to reverse engineer my first virus in 1994. While making my first
intro (a small graphics demo showing off coding skills in the day) I stumbled
upon an int 21h, sub function 40h in another intro who's fading routine I
wanted to steal. int 21h sub function 40h is the equivalent of WriteFile()
today and it had no business in an intro. Turned out the intro was infected
with Taipan. By debugging and disassembling a virus that had already infected
our system was ok with the house rules, at least the way I bend them. So using
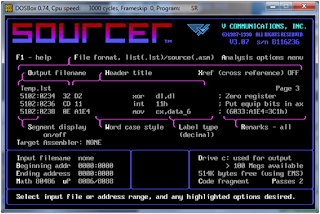
the Game Tools Debugger, Softice Debugger and Sourcer disassembler I took apart
the virus. Sourcer was the IDA of the day and Softice the most powerful
debugger available. However in many cases Game Tools - a freeware debugger -
was just more convenient. Softice by NuMega was by far the best debugger in
that time period, however it spend too much memory and was unable to debug
protected mode code that used the DOS4GW dos extender. For those reasons a
great many times one would stray to Game Tools for real mode stuff and to the
Watcom Debugger for protected mode stuff. This debugger came with the Watcom C
compiler which was behind the DOS4GW so called dos extender. The Watcom
debugger was however always very buggy, crashing all the time. Also in this
period of time there where only one book you needed to own. Assembly Language
Master Class (Wrox Press Master Class) and my roommate Mads owned a copy that
where constantly being explored by yours truely.
1995 - 2000
1995 was
of cause the year where Windows 95 came out and it was a game changer. It was
the final architecture change to protected mode. It was also the year where
internet became more than a VAX/VMS connection to "lynx", a text
based HTML browser and almost no valuable information to find anywhere. I found
my way to EFFNET on IRC and and met a large number of fellow assembler freaks
and that boosted possibilities again to the power of 10. I had documentation,
help, mentors, tools and uncharted
territory everywhere. One of the things I quickly became interested in was
writing executable packers and crypters. There was a mailing list in the
day for executable packers: Rose's exelist. Game tools, sourcer and softice was
out. There could be only one debugger and that was WinIce from NuMega and
anybody familiar with Softice could easily migrate. Obvious writting executable
encrypters immediately meant defeating debuggers - especially Winice. I spend
hours writing code to detect winice in all sort of devious ways. Not long after Mads bought Matt
Pietrek's "Windows 95 System Programming Secrets". At first I didn't
understand the book, and it my second go I immediately knew that the cool
things he was doing, I could do too. Winice, lot's of coca cola and every
secret in Windows 95 was mine. Even after Win2k came out Privilege elevation
was so trivial that it wasn't even considered a feat unless it was particularly
spectacular. Buffer overflows were in vogue and a dozen a dime. I remember
Halvar Flake used to say: Find me a sprintf and I'll give you an exploit. That
wasn't quite true, but not far from it. And it was then I (semi-) retired as a malware
hobbyist and started working as a programmer. Ironically as the malware era had really
just begun.
act-13.txt
can be found here: http://web.textfiles.com/hacking/act-13.txt
New Brain
picture was stolen from Wikipedia.com
Machine
code monitor picture was shamelessly stolen from C-64 Wiki.



The reproduction of another manufacturer's products following it original design and manufacturing process is called reverse engineering. Reverse engineering will help you to revel your competitor products and enhance the quality of your products. Reverse engineering Calgary, Alberta
ReplyDeleteThanks for sharinng
ReplyDelete