Samsung Electronics has numerous TV models on sale across different price ranges and fulfilling different purposes. Most are conventional TVs. Others are “lifestyle” TVs meant to enhance the look of your home or provide features like automatic rotation between landscape and portrait form factors. But at the heart of it all is the display itself. Samsung uses a few display technologies for its TVs, including QLED, QD-OLED, and Micro LED.
These display technologies are fundamentally different, and it's worth knowing how they function and which one is superior to the others. Next up, we'll look at each display technology individually and explain how it works.
What is QLED display technology?
A QLED TV display works similarly to LCD. QLED has an LED backlight, a polarizer, and a color filter, among other layers. The main difference between QLED and LCD TVs is that the former uses a Quantum Dot Enhancement Film, or QDEF, in front of the Blue LED backlight.
This QDEF layer converts some of the blue light to achieve pure white light. This method can deliver improved brightness and a wider color gamut for HDR. One of the advantages of QLED panels is that they have less backlight bleed compared to LED or Mini LED displays (not to be confused with Micro LED panels, but more on that later).
In essence, a QLED TV works kind of like LCDs, generating colors through color filters and a polarizer. However, it also uses quantum dots as a backplane technology behind the LCD, which helps brightness and HDR performance. You'll find this display technology in Samsung's more attainable TVs.
What is QD-OLED display technology?
Before we go into QD-OLED panels, it's very important to keep in mind that OLED TV panels and (AM)OLED smartphone displays are very different. While OLED smartphone screens have red, green, and blue self-emissive subpixels, OLED TV panels still use a color filter for color conversion, similar to LCDs. But unlike OLED and QLED, QD-OLED TV panels use quantum dots instead of color filters to convert colors on subpixels.
Quantum dots are small nanocrystals that absorb photons and emit new ones in different colors. The resulting color differs depending on the size of the quantum dot. The smallest quantum dots emit blue light, while the largest quantum dots emit red light, with color variations between the smallest and largest dots.
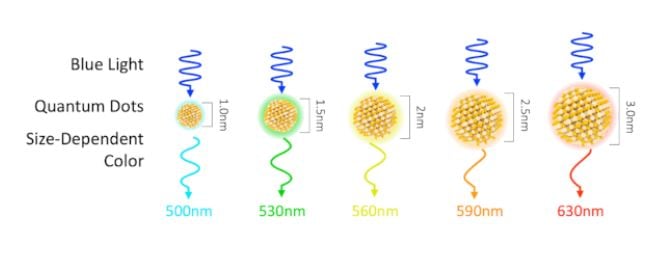 As mentioned above, QLED panels use quantum dots to convert some of the blue light emitted by LEDs to achieve white light. But QLED panels still need a color filter and a polarizer, and QD-OLED screens are different in this regard.
As mentioned above, QLED panels use quantum dots to convert some of the blue light emitted by LEDs to achieve white light. But QLED panels still need a color filter and a polarizer, and QD-OLED screens are different in this regard.
QD-OLEDs use quantum dots to convert blue light from an OLED array to other colors without needing a traditional color filter and a polarizer. And although QD-OLED technology is not the same as AMOLED, it's closer to it than regular OLED or QLED TV displays are.
In the end, it's important to keep in mind that QD-OLED panels are not the same as QLED, even though both use quantum dot technology. They use it in different manners, and technically speaking, QD-OLED panels rely more on quantum dots than QLEDs do to create colors. QLED uses quantum dots for white light and better HDR, while QD-OLED uses quantum dots for color reproduction. Samsung's latest premium TVs feature QD-OLED panels.
QLED vs QD-OLED: Advantages and disadvantages
The nitty-gritty of how these TV display technologies work aside, both QLED and QD-OLED have advantages and disadvantages in the real world.
Generally speaking, QLED TV displays have a wider color gamut and are brighter than QD-OLED, but QD-OLED displays have better contrast and deeper black levels, similar to smartphone AMOLED screens.
What is Micro LED display technology?
One of the most important aspects to consider when discussing Micro LED display technology is that it is very different from Mini LED.
You can think of Mini LED as a backlight technology. It's an array of white Mini LEDs that offers more control over the backlight of LCD displays through many more dimming zones.
In contrast, Micro LED display technology is emissive, similar to AMOLED. A Micro LED panel features tiny individual colored Micro LEDs that make up the color image and emit light. It's as close to a smartphone's AMOLED as you can get in the TV market.
Micro LED display technology offers excellent color reproduction, viewing angles, and perfect blacks. In theory, Micro LED TVs have the best image quality, beating QD-OLED and QLED. It seems to be the way of the future for Samsung TVs.
The downside is that Micro LED displays are considerably more expensive than QLED and QD-OLED. But as the technology matures, it should become more affordable, eventually. Micro LED panels are currently used in some of Samsung's most expensive TVs.









