Bedbugs

Furniture, wallpaper, mattresses, and clutter provide nesting spots for these small, flat insects. They like to live near people or pets, and they come out while you’re asleep to feed on your blood. Bedbugs don’t cause disease, but you might have an allergic reaction to their bite. If you scratch too much, the bitten area could get infected. Use antiseptic creams or lotions, or take an antihistamine, to ease the itch.
Lice

These insects live on your blood. There are three types: head, body, and pubic. Only body lice spread diseases. Since they crawl, you can get lice through close contact with someone. They lay eggs on you, and the itching starts when they hatch. You can treat them with over-the-counter and prescription medications and shampoos.
Scabies

A mite that digs into your body and lays eggs causes this condition. You get it from skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. Symptoms include itching at night, a pimply rash, sores, and crusty patches. You can treat it with a prescription medicine that kills the mites called scabicide.
Pork Tapeworms
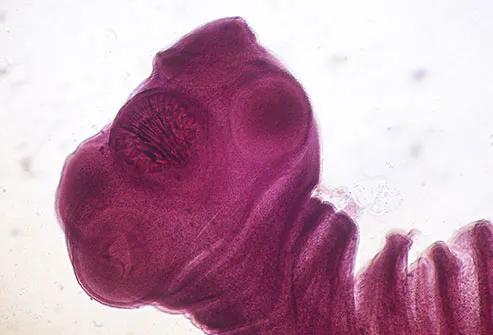
You can't get these bugs from eating pork, unless it's raw or undercooked. Both people and pigs carry them, but they're spread when you swallow the eggs from tainted food and water. You can also get them if you come in contact with the feces of someone who has them. They infect the intestines and brain, which can lead to a disease that causes headaches and seizures, called cysticercosis. Some people get better without treatment. Others need medication or surgery.
Brain-Eating Amoeba
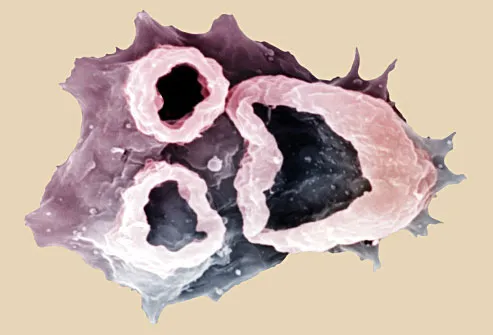
People in the U.S. don't have to worry as much about this parasite as people in Southeast Asia do. The bug, also known as N. fowleri, lives in warm freshwater, and it enters the body through the nose. It causes a condition that destroys brain tissue called primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Symptoms include headache, fever, vomiting, confusion, stiff neck, seizures, and loss of balance. Only experimental treatments are available now, so the survival rate is low.
Roundworms
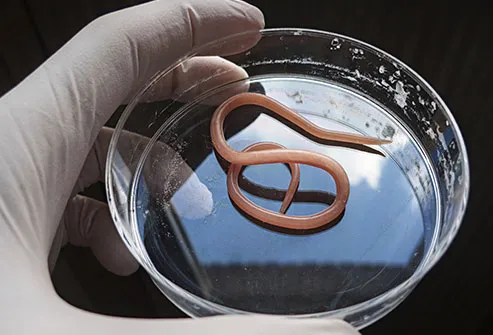
Most of these bugs infect your intestines. But the one that causes trichinosis also affects your muscles.
Common roundworm diseases and their symptoms include:
- Ascariasis -- belly pain
- Hookworm -- blood loss
- Pinworm -- anal itching
- Trichinosis -- pain, fever, face swelling, pink eye, rash
- Whipworm -- mucus, water and blood in stool, rectal prolapse (when part or all of the rectum slides out of place)
Your doctor may prescribe drugs to treat these infections.
Giardia

If you've ever been camping and you came down with diarrhea, gas, stomach cramps, bloating, and nausea, you’ve likely caught this bug. You get it through food or drinking water, or from contact with the feces of an infected person or animal. The illness can be treated with prescription drugs.
T. cruzi
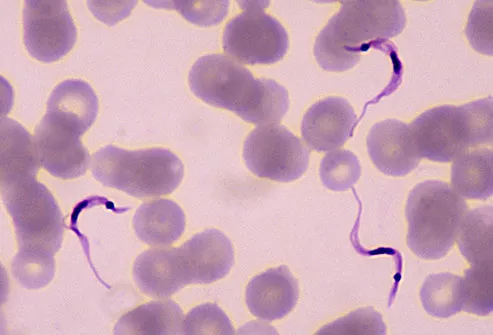
This parasite causes Chagas disease, which can be life-threatening. People get infected from contact with the bug’s feces. Symptoms show up quickly as fever, fatigue, aches, headache, rash, loss of appetite, diarrhea, vomiting, and swollen eyelids. Later, it can lead to heart and intestine problems. Doctors treat the disease and kill the parasite with medication.
Cryptosporidium
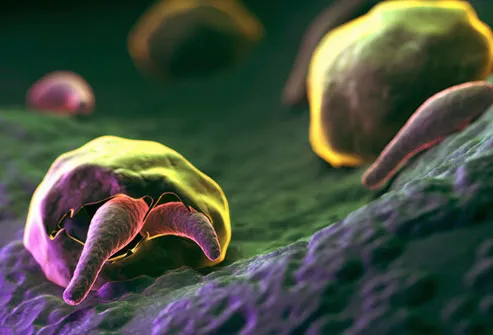
This bug's also called "crypto," and it affects your intestines. It’s spread by contact with the stool of an infected person or animal. People tend to catch it from pool water, especially kids. The diarrhea it causes can last a long time, but it usually goes away on its own without treatment.
P. Falciparum
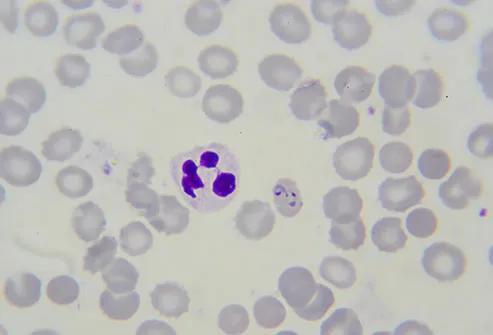
Some mosquitoes carry this parasite, which causes malaria. The disease kills more people than any other of its kind. It feels like the flu, and it causes body chills, fever, and sometimes nausea or vomiting. A doctor has to look at someone's blood under a microscope to tell if they have it. Early treatment is best. Certain prescription drugs can cure most types.
T. Vaginalis
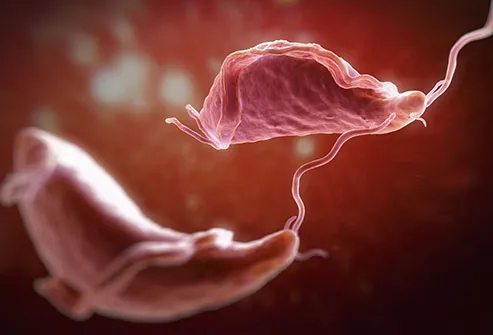
This parasite causes a sexually transmitted disease called trichomoniasis, the most common curable STD. Most infected people don’t have any symptoms, but some may notice itching, burning, or irritation of their penis or vagina. It’s treated with antibiotics.
D. Fragilis

Doctors aren't sure how you get this parasite, which infects your large intestine. Some people have stomach pain and diarrhea, but others have no symptoms. It's common in all parts of the world. Your doctor can prescribe medicine to help you get rid of it.
Toxoplasma
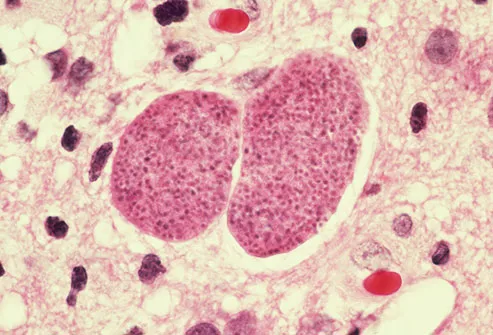
This bug makes its home in meat, water, and infected cat feces. It causes an illness called toxoplasmosis, which can feel like the flu. Pregnant women and people with weak immune systems can have serious symptoms, like cysts in the muscles, brain, and eyes. Usually it isn't treated, but a doctor can prescribe medication for a severe infection.
Guinea Worm

This roundworm's days of spreading disease are nearly done, thanks to health groups that teach people how to avoid getting infected. People catch the bug by drinking water from ponds infected with larvae. The worms mate and grow in the stomach, then burst out through a blister on the skin. Symptoms can include fever, swelling, and pain near the blister, but it usually takes a year after infection for warning signs to show up. There’s no treatment.
Good-Guy Parasites?

Parasites do a whole lot of bad, but some researchers are trying to find out if they might be used for good, too. Studies of "worm therapy," in which you swallow parasite eggs to treat disease, show it helps relieve symptoms of colitis, Crohn’' disease, type 1 diabetes, and asthma. It’s still experimental in the U.S.
Parasites: See What's Eating Your Skin
This tool does not provide medical advice. See additional information: 
© 1996-2024 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on WebMD
