Dog Skin Problems

The sound of a dog constantly scratching or licking can be as irritating as nails on a chalkboard. But don't blame your pooch for these bad habits -- a skin condition is probably the culprit. Possible causes range from parasites to allergies to underlying illness. WebMD has compiled images of some of the most common canine skin problems.
Allergic Dermatitis
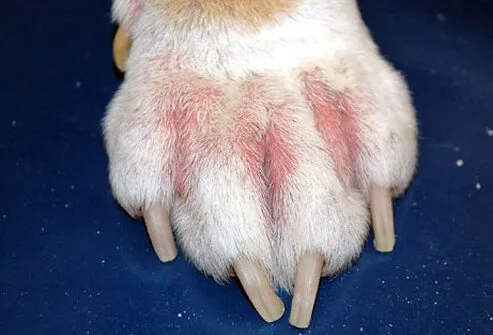
Dogs can have allergic reactions to grooming products, food, and environmental irritants, such as pollen or insect bites. A dog with allergies may scratch relentlessly, and a peek at the skin often reveals an ugly rash. Corticosteroids can help with itchy rashes, but the most effective treatment is to identify and avoid exposure to the allergens.
Yeast Infection
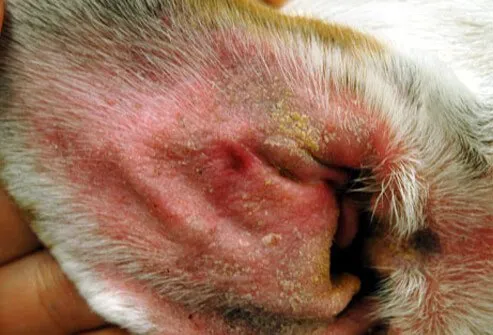
If your dog can't seem to stop scratching an ear or licking and chewing her toes, ask your veterinarian to check for a yeast infection. Symptoms include irritated, itchy, or discolored skin. The infection usually strikes the paws or ears, where yeast has a cozy space to grow. Yeast infections are easy to diagnose and often respond well to a topical cream. In some cases, your veterinarian may prescribe oral drugs or medicated baths.
Folliculitis

Superficial bacterial folliculitis is an infection that causes sores, bumps, and scabs on the skin. These skin abnormalities are easier to see in shorthaired dogs. In longhaired dogs, the most obvious symptoms may be a dull coat and shedding with scaly skin underneath. Folliculitis often occurs in conjunction with other skin problems, such as mange, allergies, or injury. Treatment may include oral antibiotics and antibacterial ointments or shampoos.
Impetigo
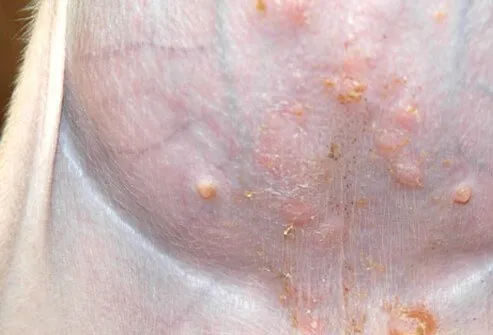
Another type of bacterial infection, impetigo is most common in puppies. It causes pus-filled blisters that may break and crust over. The blisters usually develop on the hairless portion of the abdomen. Impetigo is rarely serious and can be treated with a topical solution. In a small number of cases, the infection may spread or persist.
Seborrhea
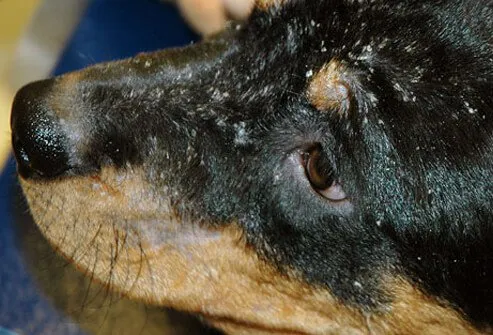
Seborrhea causes a dog's skin to become greasy and develop scales (dandruff). In some cases, it's a genetic disease that begins when a dog is young and lasts a lifetime. But most dogs with seborrhea develop the scaling as a complication of another medical problem, such as allergies or hormonal abnormalities. In these cases, it is vital to treat the underlying cause so symptoms do not recur.
Ringworm
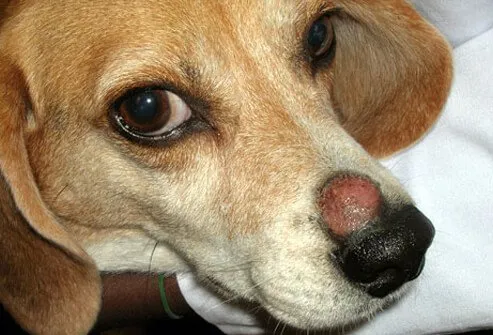
Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm, but by a fungus. The term "ring" comes from the circular patches that can form anywhere, but are often found on a dog's head, paws, ears, and forelegs. Inflammation, scaly patches, and hair loss often surround the lesions. Puppies less than a year old are the most susceptible, and the infection can spread quickly between dogs in a kennel or to pet owners at home. Various anti-fungal treatments are available.
Shedding and Hair Loss (Alopecia)

Anyone who shares their home with dogs knows that they shed. How much shedding is normal depends on breed, time of year, and environment. But sometimes stress, poor nutrition, or illness can cause a dog to lose more hair than usual. If abnormal or excessive shedding persists for more than a week, or you notice patches of missing fur, check with your veterinarian.
Mange (Mites)

Mange is a skin disorder caused by tiny parasites called mites. Sarcoptic mange, also known as canine scabies, spreads easily among dogs and can also be transmitted to people, but the parasites don't survive on humans. The symptoms are intense itching, red skin, sores, and hair loss. A dog's ears, face and legs are most commonly affected. Demodectic mange can cause bald spots, scabbing, and sores, but it is not contagious between animals or people. Treatment depends on the type of mange.
Fleas

Fleas are the bane of any pet owner. You may not see the tiny insects themselves, but flea droppings or eggs are usually visible in a dog's coat. Other symptoms include excessive licking or scratching, scabs, and hot spots. Severe flea infestations can cause blood loss and anemia, and even expose your dog to other parasites, such as tapeworms. Treatment may include a topical and/or oral flea killer and a thorough cleaning of the pet's home and yard.
Ticks

Ticks, like fleas, are external parasites that feed on the blood of their hosts. You can spot a tick feeding on your dog with the naked eye. To properly remove a tick, grasp the tick with tweezers close to the dog’s skin, and gently pull it straight out. Twisting or pulling too hard may cause the head to remain lodged in your dog’s skin, which can lead to infection. Place the tick in a jar with some alcohol for a couple of days and dispose of it once it is dead. In addition to causing blood loss and anemia, ticks can transmit Lyme disease and other potentially serious bacterial infections. If you live in an area where ticks are common, talk to your veterinarian about tick control products.
Color or Texture Changes
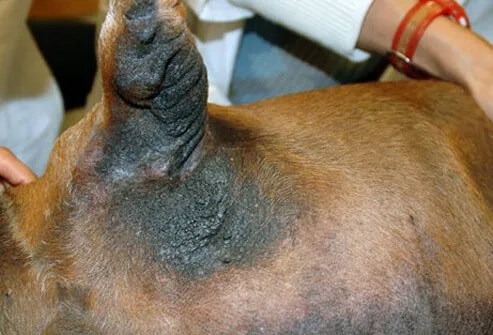
Changes in a dog's skin color or coat texture can be a warning sign of several common metabolic or hormone problems. Be sure to ask your veterinarian about any significant changes to your dog's coat.
Dry, Flaky Skin

Dry, flaky skin can be a red flag for a number of problems. It's a common symptom of allergies, mange, and other skin diseases. But most often, dry or flaky skin is nothing serious. Make sure you are feeding Fido high quality food. Like people, some dogs simply get dry skin in the winter. If this seems to cause your pet discomfort, consult your veterinarian.
Acral Lick Granuloma
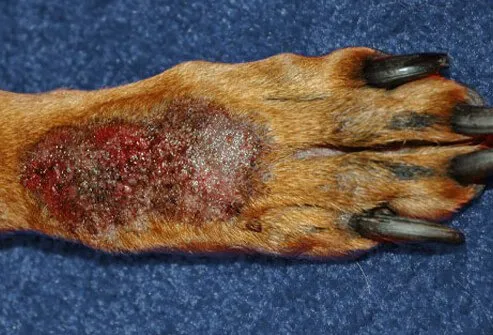
Also called acral lick dermatitis, this is a frustrating skin condition caused by compulsive, relentless licking of a single area – most often on the front of the lower leg. The area is unable to heal, and the resulting pain and itching can lead the dog to keep licking the same spot. Treatment includes discouraging the dog from licking, either by using a bad-tasting topical solution or an Elizabethan collar.
Skin Tumors

If you notice a hard lump on your dog's skin, point it out to your vet as soon as possible. Dogs occasionally develop cancerous tumors in their skin. The only way to confirm a diagnosis of cancer is to biopsy the tumor. If the lump is small enough, your veterinarian may recommend removing it entirely. This can yield a diagnosis and treatment with a single procedure. For tumors that have not spread, this may be the only treatment needed.
Hot Spots
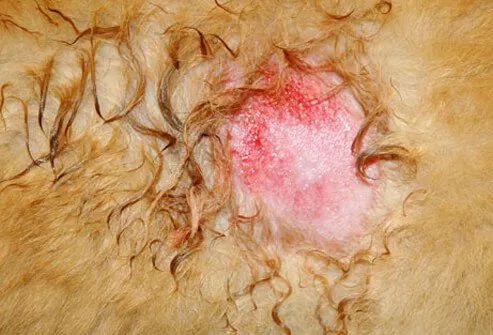
Hot spots, also called acute moist dermatitis, are small areas that appear red, irritated, and inflamed. They are most commonly found on a dog's head, hips, or chest, and often feel hot to the touch. Hot spots can result from a wide range of conditions, including infections, allergies, insect bites, or excessive licking and chewing. Treatment consists of cleansing the hot spot and addressing the underlying condition.
Immune Disorders

In rare cases, skin lesions or infections that won't heal can indicate an immune disorder in your dog. One of the best known is lupus, a disease that affects dogs and people. Lupus is an autoimmune disorder, meaning the body's immune system attacks its own cells. Symptoms include skin abnormalities and kidney problems. It can be fatal if untreated.
Anal Sac Disease

As if dog poop weren't smelly enough, dogs release a foul-smelling substance when they do their business. The substance comes from small anal sacs, which can become impacted if they don't empty properly. The hallmark of impacted anal sacs is a dog scooting his bottom along the ground. Other symptoms include biting or licking the anal area. A vet can manually express full anal sacs, but in severe cases, the sacs may be surgically removed.
When to See the Vet

Although most skin problems are not emergencies, it is important to get an accurate diagnosis so the condition can be treated. See your veterinarian if your dog is scratching or licking excessively, or if you notice any changes in your pet's coat or skin, including scaling, redness, discoloration, or bald patches. Once the cause is identified, most skin problems respond well to treatment.
Pet Health Slideshow: Skin Problems in Dogs
This tool does not provide medical advice. See additional information: 
© 1996-2024 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on WebMD
