Birth Control Basics

If avoiding pregnancy is your goal, you have many different birth control methods to choose from. You can go with barrier methods (like condoms), hormonal methods (like the pill or IUD), sterilization (a vasectomy for men or tubal ligation for women), and others. Whichever you pick, be aware of possible side effects.
Headaches
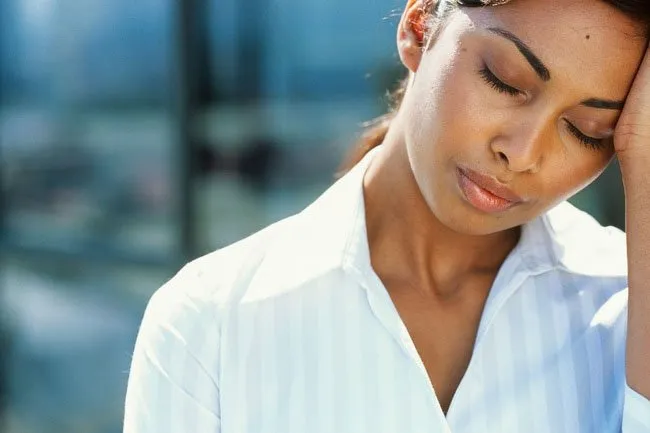

One of the most common methods of contraception is the birth control pill. One side effect that women report with all types of birth control pills is headaches. This can happen with combination birth control pills -- that contain estrogen and progestin -- and the minipill that has only progestin. But not all women get them. Those who do usually have them for 2 to 3 months. Other hormonal methods, like intrauterine devices (IUDs), patches, or injections can bring headaches too.
Nausea

The hormonal changes common with some birth control methods can bring nausea from time to time. This can happen with options like combination birth control pills, progestin-only birth control pills, the patch, the contraceptive ring, and the so-called morning-after pill that can prevent pregnancy after a birth control method fails or after unprotected sex.
Breast Tenderness
Hormones in various birth control methods show up throughout the body, stopping the release of the egg from the ovaries and causing other bodily changes that help prevent pregnancy. If you use hormonal birth control methods like the pill, the minipill (with progestin only), the patch, or the vaginal ring, breast tenderness is possible. If you feel it, the tenderness usually goes away in 3 to 5 months.
Changes in Your Period

One possible side effect from birth control methods you take by mouth (like the pill or the morning-after pill) is a difference in the bleeding during your period. The amount that you bleed could change, you might have breakthrough bleeding or spotting between periods, or you may stop bleeding completely -- either occasionally or for several months in a row. Your doctor can tell you whether what's going on is a normal side effect or something else.
Cramps
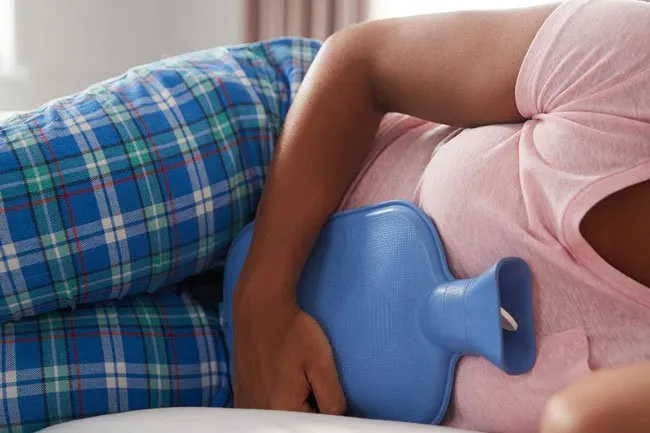

Some women who use IUDs -- they come both in hormonal and nonhormonal versions -- get cramps. They can pair with backaches for a few days after you insert the IUD, but the pain usually goes away once your body gets used to the device. Over-the-counter pain medicine (like ibuprofen or aspirin) can help. If your discomfort continues for more than a few days, check with your doctor to make sure your IUD sits where it should.
Acne

If you choose hormonal implants as your birth control method, a thin rod goes inside the skin of your upper arm. It can stay in place for up to 3 years. It's the most highly effective method of reversible birth control around (less than one pregnancy per 100 women every year). But one possible side effect from a hormonal implant is acne.
Mood Changes

The hormones in a contraceptive ring stop your body from releasing eggs from your ovaries, a process called ovulation. The hormones also thicken mucus in your cervix to keep sperm from reaching the egg. It all can also cause discomfort and discharge, as well as changes in your mood.
Weight Changes

You can take hormones for birth control many different ways. Research has shown that most methods won't cause women to gain much weight. The exception is when they take it by injection. Studies suggest that weight and fat can go up significantly with the shot. But once you stop getting the injection, the fat comes off.
Skin Allergies
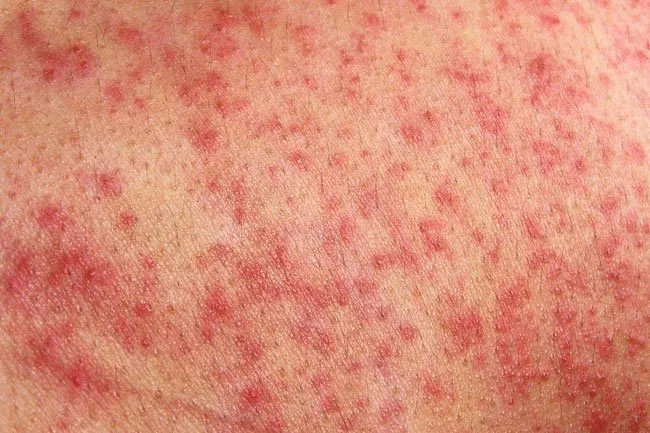
If you're allergic to latex, condoms may cause an allergic reaction. If you use a birth control patch, you might get some irritation around the area where you put it on. The vaginal ring and other methods, like sponges and cervical caps with spermicide (a chemical which neutralizes sperm) can also cause irritation and discomfort.
Smoking and the Pill

This can be a dangerous combination. If you take a pill with the estrogen in it and you already have certain health problems -- including diabetes, breast cancer, blood-clotting disorders, high blood pressure, some heart or blood vessel problems, and liver or gallbladder disease -- you may be at risk for serious, even life-threatening side effects. If you smoke, your chances of these side effects go up. Talk with your doctor about ways you can quit.
Good Side Effects

Birth control pills with hormones may lower your odds of getting certain types of cancer, including colorectal, endometrial, and ovarian cancers. Pills can ease painful, heavy periods too. They can also calm cramps, reduce cysts in your breasts and ovaries, prevent bone thinning, and help prevent anemia from iron deficiency. They may even help with acne.
What Are The Side Effects of Birth Control?
This tool does not provide medical advice. See additional information: 
© 1996-2024 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved.
Source slideshow on WebMD
