How Renault solved scaling and cost challenges on its Industrial Data platform using BigQuery and Dataflow
Jean-Francois Macresy
Consultant, Google Cloud
Jérémie Gomez
Strategic Engineer, Google Cloud
Try Google Cloud
Start building on Google Cloud with $300 in free credits and 20+ always free products.
Free trialFollowing the first significant bricks of data management implemented in our plants to serve initial use cases such as traceability and operational efficiency improvements, we confirmed we got the right solution to collect industrial data from our machines and operations at scale. We started to deploy that solution and we therefore needed a state-of-the-art data platform for contextualization, processing and hosting all the data gathered. This platform had to be scalable to deploy across our entire footprint, and also affordable and reliable, to foster the use of data in our operations. Our partnership with Google Cloud in 2020 was a key lever to reach this target.
Jean-Marc Chatelanaz - Industry Data Management 4.0 Director, Renault
French multinational automotive manufacturer Renault Group has been investing in Industry 4.0 since the early days. A primary objective of this transformation has been to leverage manufacturing and industrial equipment data through a robust and scalable platform. Renault designed an industrial data acquisition layer and connected it to Google Cloud, using optimized big data products and services that together form Renault's Industrial Data Platform.
In this blog, we’ll outline the evolution of that data platform on Google Cloud and how Renault worked with Google Cloud’s professional services to design and build a new architecture to achieve a secure, reliable, scalable, and cost-effective data management platform. Here’s how they’ve done it.
All started with Renault’s digital transformation
Renault Group has manufactured cars since 1898. Today, it is an international group with five brands that sold close to 3 million vehicles worldwide in 2020 and provide sustainable mobility throughout the world, with 40 manufacturing sites and more than 170,000 employees.
A leader in the Industry 4.0 movement, Renault launched its digital transformation plan in 2016 to achieve greater efficiency and modernize its traditional manufacturing and industrial practices. A key objective of this transformation was using the industrial data from up to 40 sites globally to promote data-based business decisions and create new opportunities.
Several initiatives were already growing in silos, such as Conditional Based Maintenance, Full Track and Trace, Industrial Data Capture and AI projects. In 2019, Renault kicked off a program named Industry Data Management 4.0 (IDM 4.0) to federate all those initiatives as well as future ones, and, most of all, to design and build a unique data platform and a framework for all Renault’s industrial data.
The IDM 4.0 would ultimately enable Renault’s manufacturing, supply chain, and production engineering teams to quickly develop analytics, AI, and predictive applications based on a single industrial data capture and data referential platform as shown with these pillars:
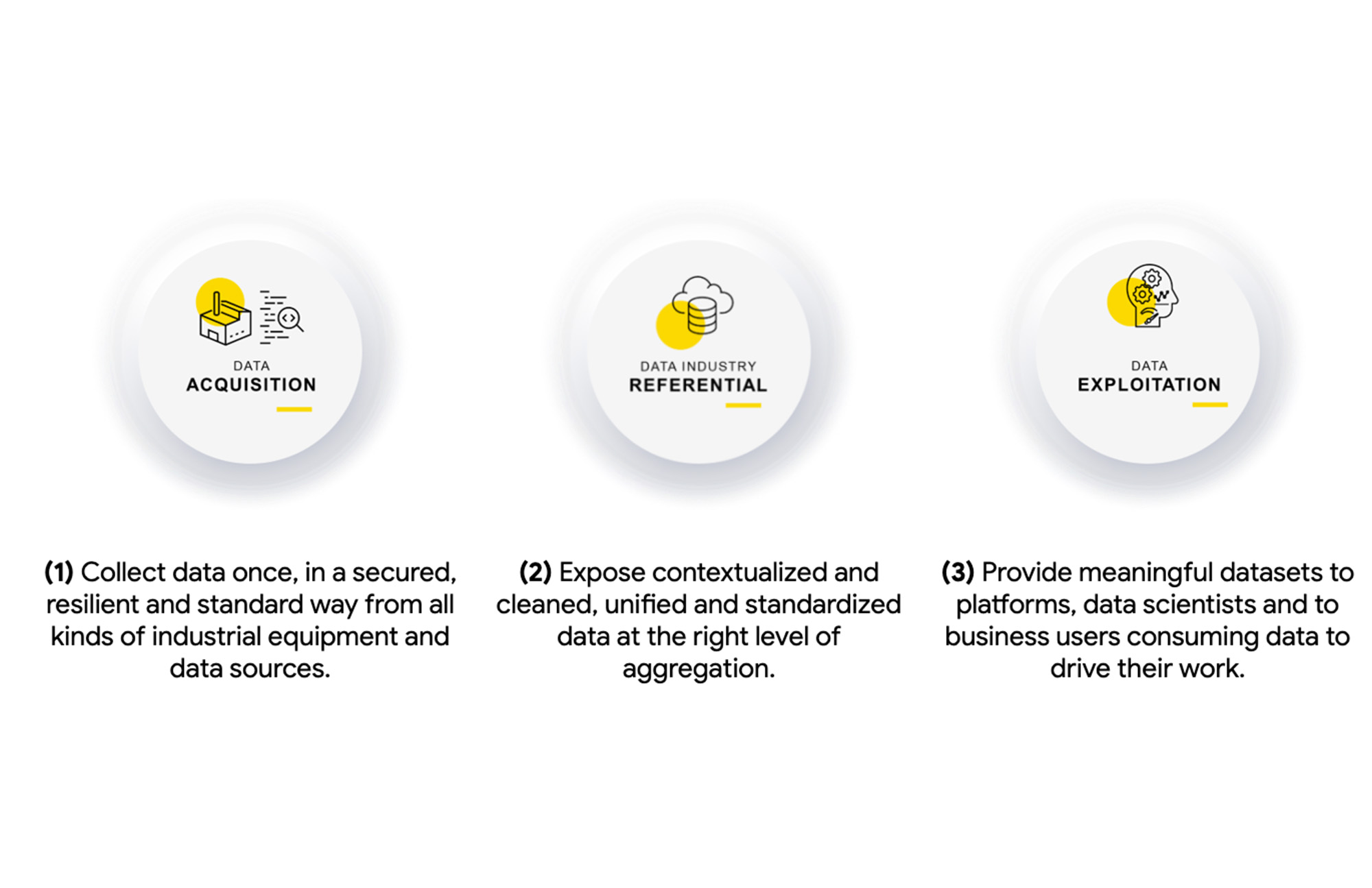

With Renault’s leadership in Industry 4.0 for manufacturing and supply chain, and with Google’s expertise in big data, analytics and machine learning since its foundations, Google Cloud solutions were a clear match for Renault’s ambitions.
Building IDM 4.0 in the cloud
Before IDM 4.0, Renault Digital was the internal team that incubated the idea of data in the cloud. Following some trials, the team was able to reduce storage costs by more than 50% by moving to Google Cloud. Key business requirements were data reliability, long-term storage, and unforgeability, all of which led the team to use Apache Spark running on fully-managed Dataproc for data processing, and Spanner as the main database.
The IDM 4.0 program aimed to scale and unfold more business use cases while keeping the platform cost-effective, with maximum performance and reliability. Meeting this goal required reviewing the architecture, as the costs projections of the business usage would go beyond the project budget, refraining from additional business explorations.
Accelerating the redesign of that core data platform was a pillar of the Renault-Google Cloud partnership. . Google Cloud’s professional services organization (PSO) helped define the best architecture to meet requirements, solve challenges, and handle 40 plants’ worth of scaling data in a reliable and cost-sustainable way.
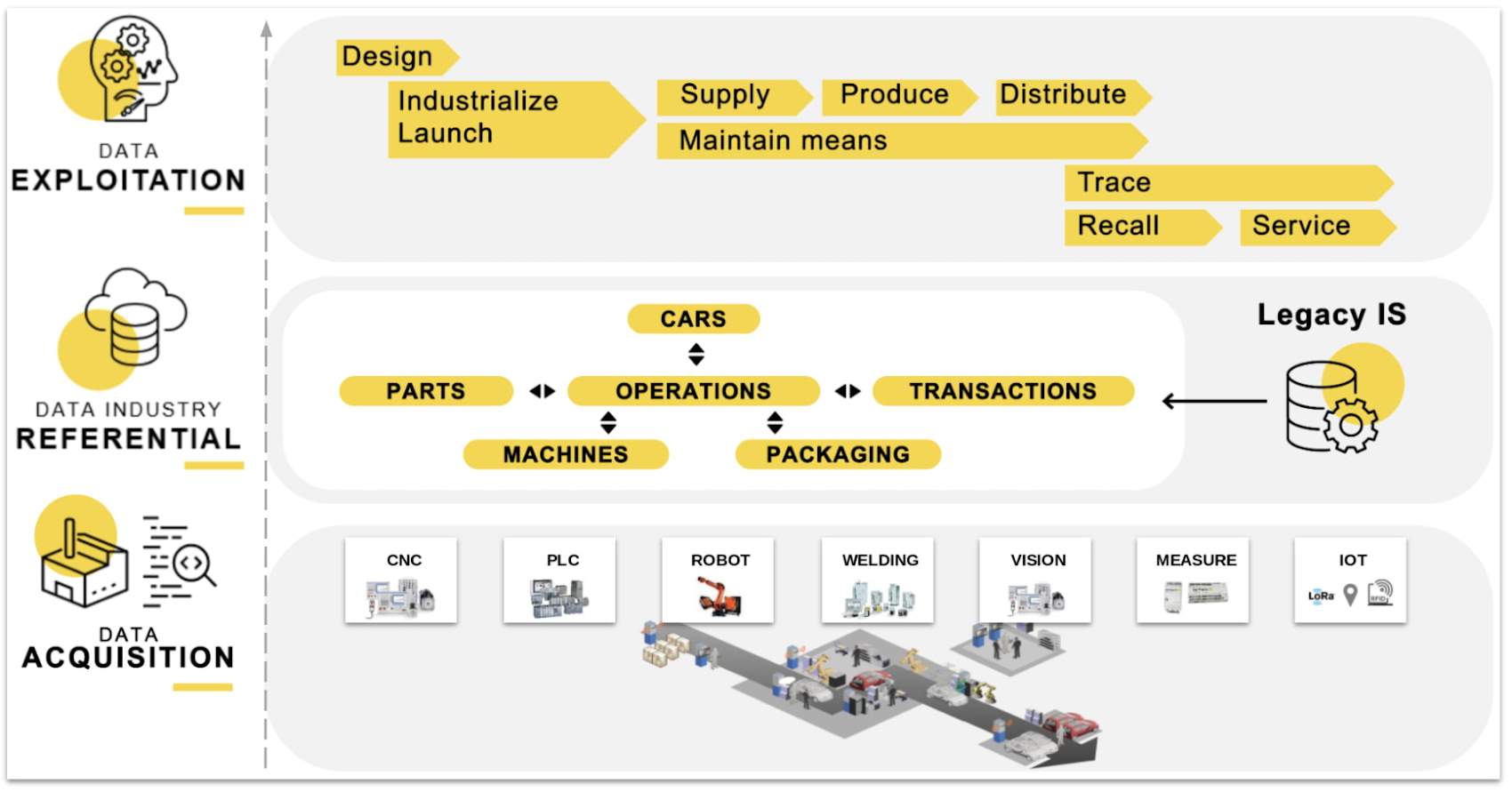

The data capture journey is complex and includes several components. Basically, Renault built a specific process relying on standard data models designed with OPC-UA, an open machine-to-machine communication protocol. In the new Google Cloud architecture, this data model is implemented in BigQuery such that most writes are append-only and it is not necessary to do lots of join operations to retrieve the required information. BigQuery is complemented with a cache in Memorystore to retrieve up-to-date states at all times. This architecture enabled high-performing and cost-efficient reads and writes.
The team also started developing with the Beam framework and Dataflow. Working with Beam was not only as easy as working with Spark, but also unlocked a number of benefits:
A unified model for batch and streaming processing: less coding variety and more flexibility in choosing the types of processing jobs depending on needs and cost target
A thriving ecosystem around Beam: many available connectors (PubsubIO, BigQueryIO, JMSIO, etc)
Simplified operations: efficient autoscaling, smoother updates, finer cost tracking, easy monitoring, end-to-end testing, and error management.
Dataflow has since become the go-to tool for most data processing needs in the platform. Pub/Sub was also a natural choice for streaming data processing, along with other third-party messaging systems. The teams are also maintaining their advanced use of Google Cloud’s managed services such as Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Cloud Composer, and Memorystore.
The new platform is built to scale, and as of Q1 2021, the IDM 4.0 team has been connecting more than 4,900 industrial appliances through Renault’s internal data acquisition solution, transmitting more than 1 billion messages per day to the platform in Google Cloud!
Focusing on cost efficiency
While the migration to the new architecture was ongoing, cost optimization became a key decision driver, especially with the COVID-19 pandemic and its impacts on the world’s economics.
Hence, Renault’s management team and Google Cloud’s PSO agreed to allocate a special task force to optimize costs on parts of the platform that were not yet migrated.
This special task force discovered that one Apache Spark cluster continuously performed Cloud Storage Class A & B operations every few tens of milliseconds. This was inconsistent with the majority of incoming flows, which were hourly or daily batches. One correction we applied was simply increasing the interval polling the filesystem, i.e. the spark.sql.streaming.pollingDelay parameter from Spark. Later, we confirmed a 100x drop in Cloud Storage Class A calls, and a meaningful drop in class B calls, which resulted in a 50% decrease in production costs.
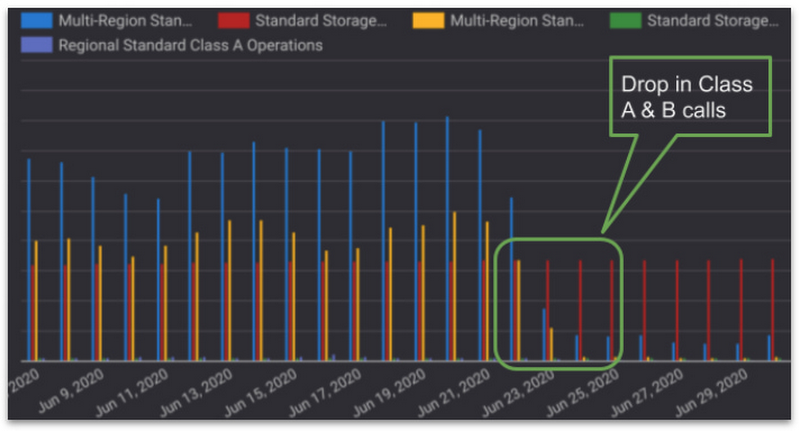

Renault now uses Dataflow to ingest and transform data from manufacturing plants as well as from other connected key referential databases. BigQuery is used to store and analyze massive amounts of data, such as packages and vehicle tracking, with many more data sources in the works.
The below diagram shows last year’s impressive achievements!
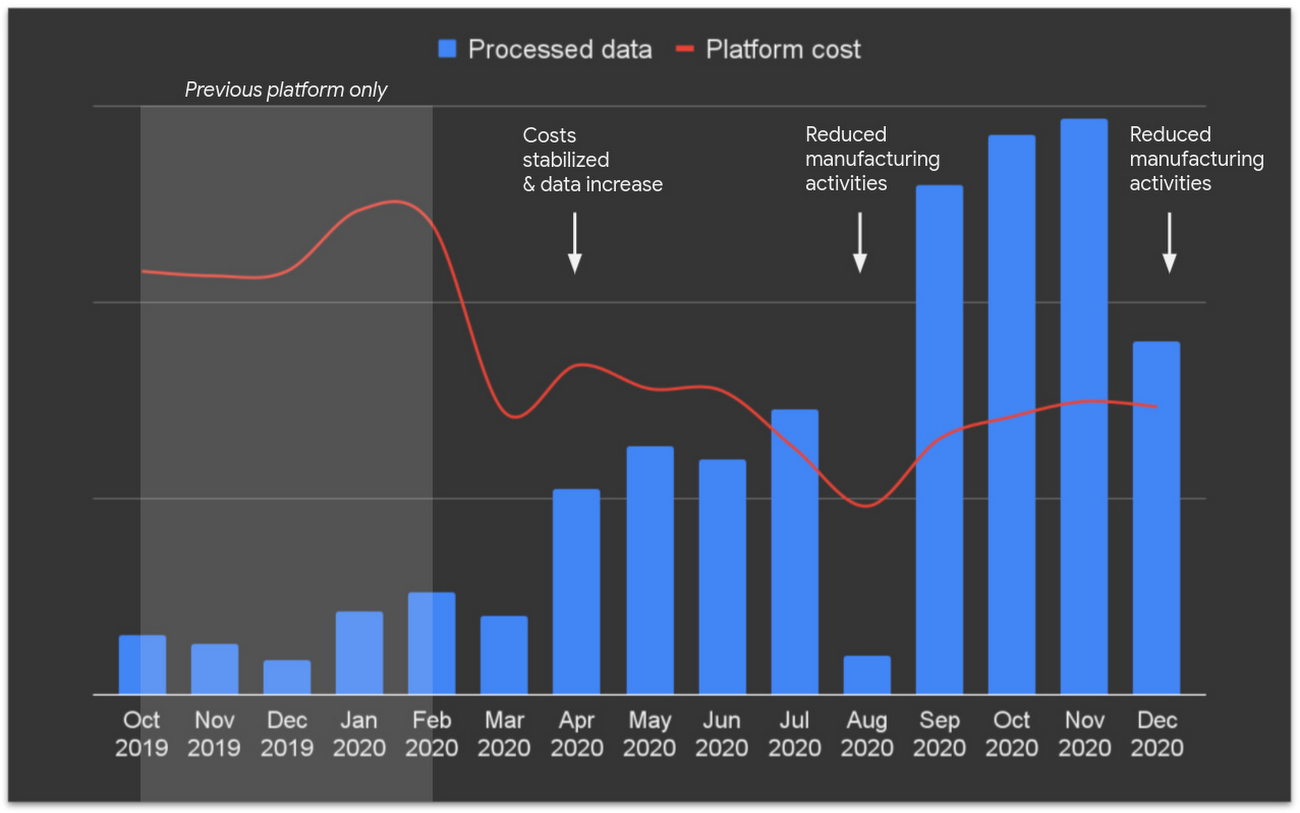

The new IDM 4.0 platform started to run production workloads just a few months ago, and Renault expects to have 10 times more industrial data coming in the next two years, helping to keep costs, performance, and reliability optimum.
Unfold new opportunities and democratize data access
The IDM 4.0 team has succeeded in gathering industrial data from plants, and merging and harmonizing this data in a scalable, reliable, and cost-effective platform. The team also managed to expose data in a controlled and secure way to data scientists, business teams or any application.
In this blog, we’ve overviewed use cases ranging from tracking to conditional maintenance, but this platform can open many other possibilities for innovation and business impact, such as self-service analytics that will democratize the use of data and support data-driven business decisions.
This Renault data transformation with Google Cloud demonstrates the potential of Industry 4.0 to improve Renault’s manufacturing, process engineering, and supply chain processes—and also provides an example for other companies looking to leverage data and cloud platforms for improved results. To learn more about BigQuery, click here.
Acknowledgments
We’d like to thank all collaborators who participated actively in writing these lines; both from Google and Renault working tremendously as one team for 1+ year, fully remote:
Writers from Google:
- Jean-Francois Macresy, Consultant, IDM4.0 Architecture best practices
- Jeremie Gomez, Strategic Engineer, IDM4.0 Data specialist
- Rifel Mahiou, Program Manager, IDM4.0 Partnership strategy & governance
- Razvan Culea, Data Engineer, IDM4.0 Data optimization
Reviewers from Renault:
- Sebastien Aubron, IDM4.0 Program Manager
- Jean-Marc Chatelanaz, IDM4.0 Director
- Matthieu Dureau, IDM4.0 platform Product Owner
- David Duarte, IDM4.0 platform Data Engineer




