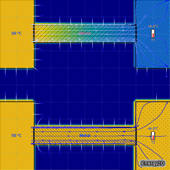
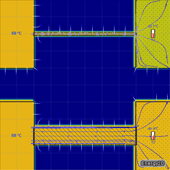
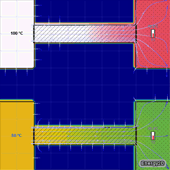
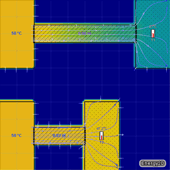
The amount of thermal energy ΔQ transferred through an area A per unit time Δt is called the heat flux. In the case of conduction, the heat flux is governed by the following relationship:
ΔQ/Δt=-kAΔT/Δx
where ΔT is the temperature difference along a distance Δx in the direction of conduction and k is the thermal conductivity of the material. This is known as Fourier's Law of Heat Conduction.
Properties of some materials:
| Material | Conductivity (W/m·°C) | Specific heat (J/kg·°C) | Density (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water (20°C) | 0.58 | 4181 | 1000 |
| Air (20°C) | 0.024 | 1012 | 1.024 |
| Copper | 401 | 385 | 8940 |
| Foam | 0.08 | 1300 | 30-120 |
The following simulations examine how each of these factors affects the rate of heat conduction. Click an image to open the corresponding simulation.